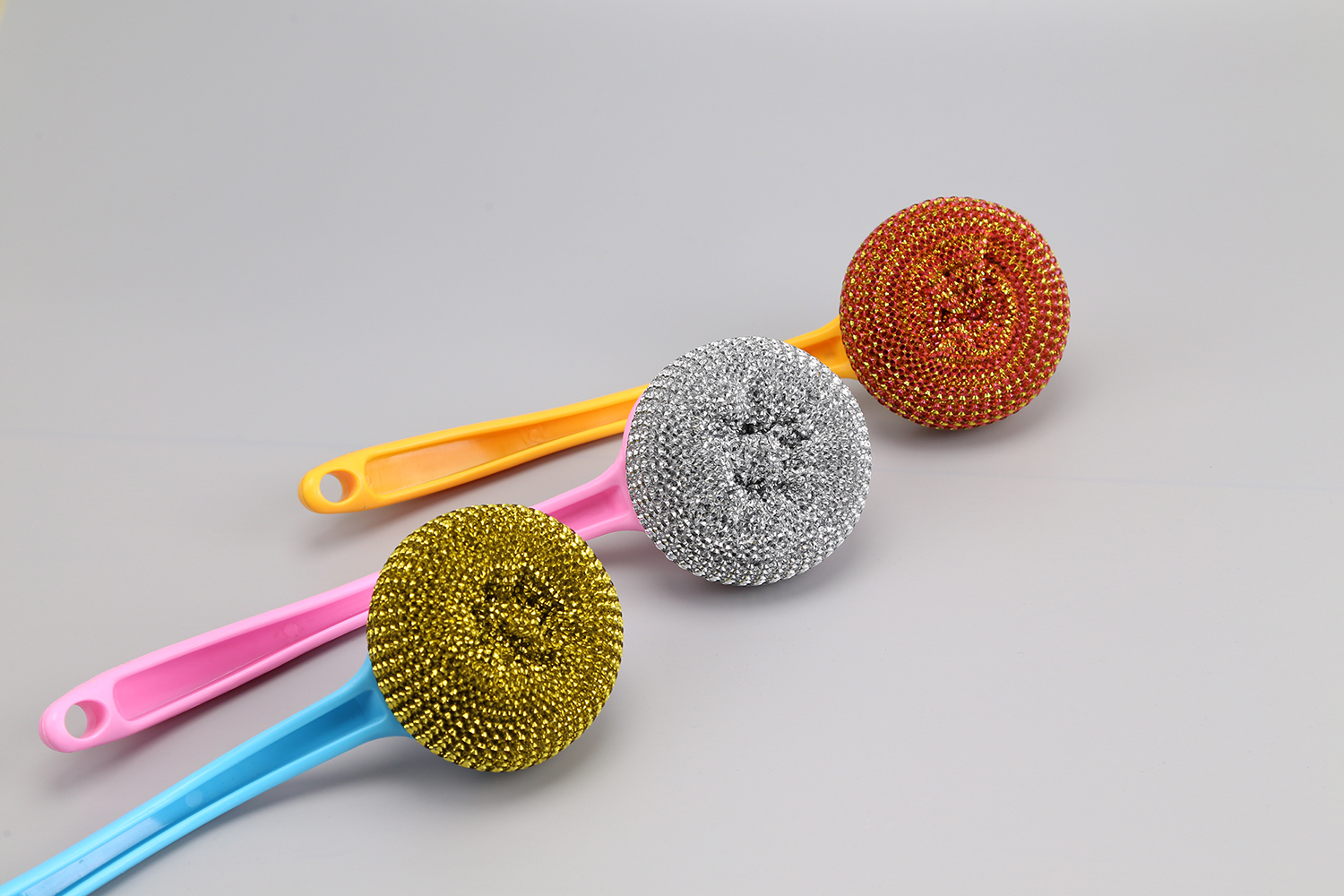
Polyester fiber (POLYESTER FIBERS), commonly known as "polyester fiber". It is a synthetic fiber obtained by spinning polyester, which is polycondensed from organic dibasic acid and diol, and is referred to as PET fiber, which is a polymer compound. Invented in 1941, it is currently the largest variety of synthetic fibers.

Compared with natural fibers, polyester has the disadvantages of low moisture content, poor air permeability, poor dyeability, easy pilling and fuzzing, and easy staining. In order to improve these shortcomings, chemical modification and physical deformation methods are adopted.
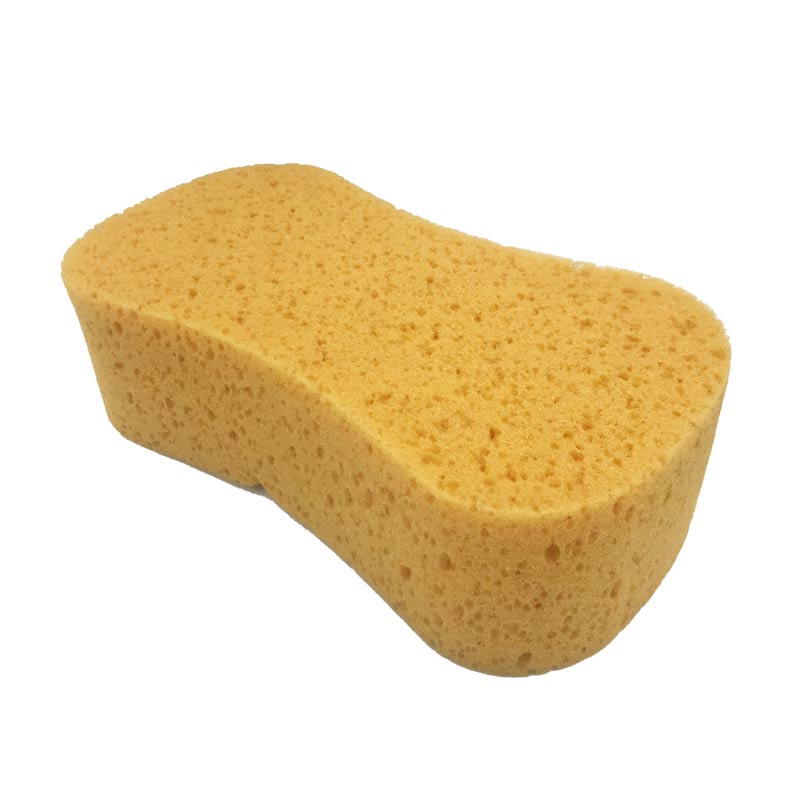
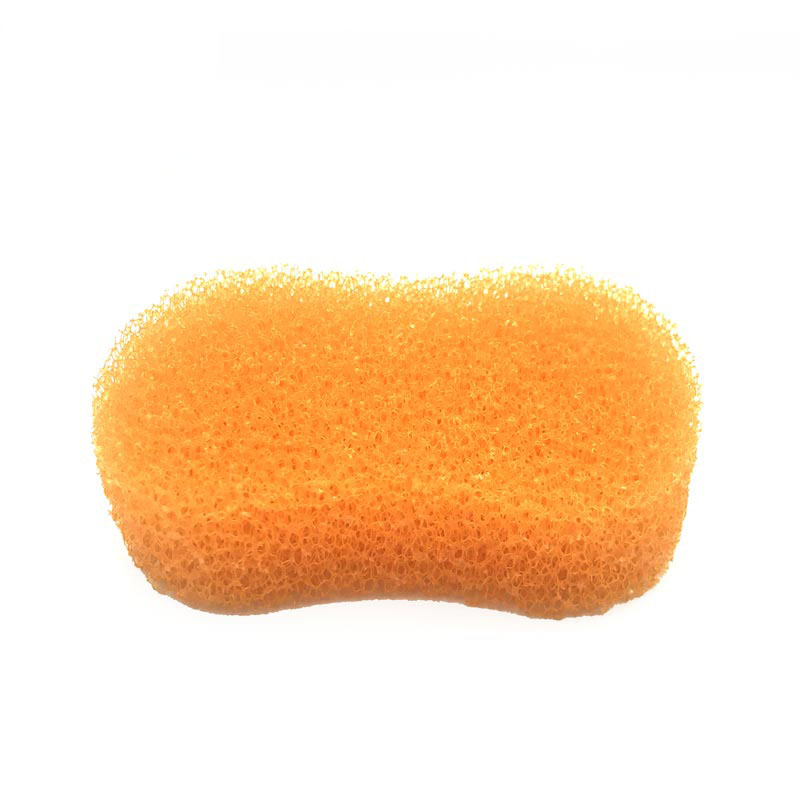
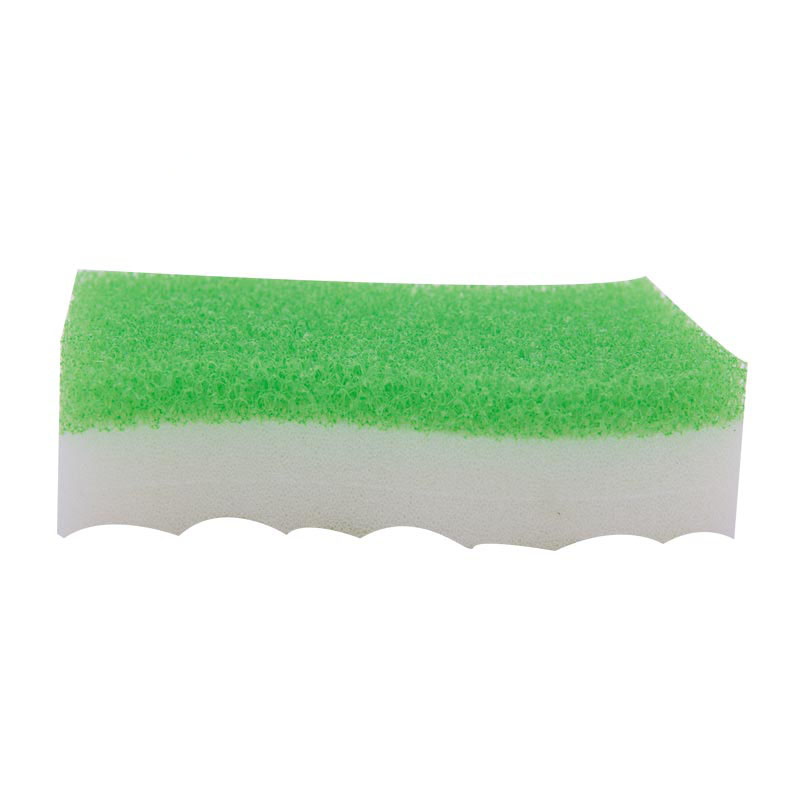
Commonly used sponges are made of wood cellulose fibers or foamed plastic polymers. In addition, there are also natural sponges made of sponge animals. Most natural sponges are used for body cleaning or painting.
In addition, there are three types of synthetic sponges made of other materials, namely low-density polyether (non-absorbent sponge), polyvinyl alcohol (high-absorbent material without obvious pores) and polyester.
The specific gravity of polyester is 1.38; the melting point is 255~260℃, it starts to bond at 205℃, the safe ironing temperature is 135℃; the moisture absorption is very low, only 0.4%; the breaking strength of filament is 4.5~5.5g/d , Short fiber is 3.5 ~ 5.5 g/denier; the elongation at break of filament is 15 ~ 25%, and the short fiber is 25 ~ 40%.
The high-strength fiber has a strength of 7-8 g/denier and an elongation of 7.5-12.5%. Polyester has excellent wrinkle resistance, elasticity and dimensional stability, good electrical insulation properties, resistance to sunlight, abrasion, mildew and decay, good resistance to chemical reagents, and resistance to weak acids and weak bases. At room temperature, it has a certain resistance to dilute and strong acids, but it has poor resistance to strong alkalis.
The dyeing performance of polyester is poor, and it is generally required to be dyed with disperse dyes under high temperature or the presence of a carrier.




















 English
English 简体中文
简体中文











